Introduction
Navigating the world of hazardous areas can feel like trying to find your way through a maze—especially when it comes to understanding hazardous area junction boxes. These specialized enclosures are designed to safely house electrical connections in environments where flammable gases or dust may be present. By ensuring that you grasp the nuances of hazardous area classifications, you're taking the first step toward making informed decisions about safety and compliance.
Understanding Hazardous Area Classifications
Hazardous area classifications categorize environments based on the likelihood of explosive atmospheres occurring, with Zone 0, 1, and 2 being key terms in this classification system. Zone 0 indicates a location where an explosive gas-air mixture is continuously present; Zone 1 is where such a mixture is likely to occur; and Zone 2 is where it’s unlikely but still possible under certain conditions. Understanding these zones is crucial for selecting appropriate equipment and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Importance of Choosing the Right Junction Box
The choice between different types of junction boxes can significantly impact safety in hazardous environments. Selecting the right junction box—whether it's Exd or Exe—can mean the difference between preventing an explosion and facing dire consequences. With questions like “Which is better, Exd or Exe?” often arising, knowing how each type functions within their respective hazardous area classifications becomes essential.
Overview of ATEX Compliance
ATEX compliance refers to regulations set forth by the European Union regarding equipment used in potentially explosive atmospheres, including specifications for hazardous area junction boxes. This compliance ensures that products meet stringent safety standards designed to protect both workers and facilities from accidents caused by ignition sources in classified zones. Familiarity with ATEX guidelines will help you navigate what are the rules for junction boxes effectively while also aligning with what is the electrical code for junction boxes.
What is Zone 0, 1, and 2 Hazardous Area Classification?

Understanding the distinctions between Zones 0, 1, and 2 is crucial for ensuring safety in environments where explosive gases or vapors may be present. These classifications help determine the appropriate use of hazardous area junction boxes and inform decisions on whether exd or exe protection methods are necessary. By grasping what these zones entail, industries can better navigate compliance with electrical codes and regulations.
Defining the Zones
Zone classifications categorize areas based on the likelihood of explosive atmospheres occurring during normal operations. Zone 0 is defined as an area where an explosive gas-air mixture is continuously present or present for long periods; this zone demands the highest level of protection due to its constant risk. Zone 1 refers to areas where such mixtures are likely to occur intermittently during normal operations, while Zone 2 encompasses locations where these mixtures are unlikely but could occur under abnormal conditions.
These definitions serve as a foundation for selecting appropriate junction boxes that meet safety standards. For example, hazardous area junction boxes used in Zone 0 must offer robust protection against ignition sources since they are exposed to potentially explosive environments at all times. In contrast, equipment suitable for Zone 2 may have less stringent requirements but still needs to adhere to specific electrical codes for junction boxes.
Real-World Examples
To put these zones into perspective, consider a petroleum refinery: Zone 0 might exist near storage tanks that contain flammable liquids continuously emitting vapors. In contrast, a chemical processing facility could classify areas around mixing stations as Zone 1 due to occasional leaks or releases of volatile substances during operation. Meanwhile, maintenance corridors or equipment rooms not typically exposed to hazardous materials would fall under Zone 2 classification.
These real-world examples illustrate how critical it is for companies operating in such environments to understand which zone their operations fall into when selecting equipment like hazardous area junction boxes. Choosing the right box type—be it exd (flameproof) or exe (increased safety)—is essential in mitigating risks associated with each zone's unique characteristics and potential hazards.
Application in Industries
Different industries apply these hazardous area classifications based on their specific needs and operational risks. The oil and gas sector often deals with Zones 0 and 1 due to volatile materials handled daily; thus, they require specialized hazardous area junction boxes designed for maximum safety and reliability in those conditions. Likewise, industries like pharmaceuticals may encounter similar challenges when dealing with flammable solvents or gases during production processes.
Moreover, understanding what is Zone 0, 1, and 2 hazardous area classification helps organizations comply with regulations while also considering which protective measures—like choosing between exd or exe—are best suited for their applications. By adhering strictly to installation guidelines outlined by electrical codes for junction boxes within these zones, companies can significantly reduce the risk of accidents related to explosions or fires caused by improper equipment selection.
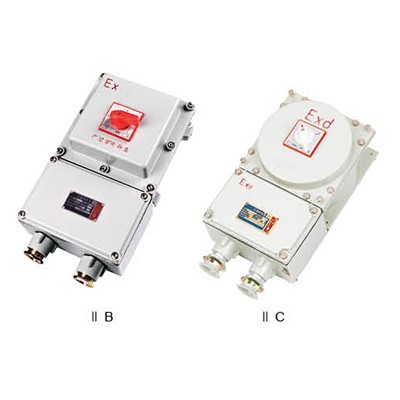
Understanding Hazardous Area Junction Boxes

When it comes to electrical installations in hazardous environments, the choice of junction boxes is paramount. Hazardous area junction boxes are specially designed to prevent ignition sources in areas where flammable gases or dust may be present. These boxes are not your standard electrical enclosures; they come with unique features tailored for safety and compliance.
What Makes Them Different?
The primary distinction of hazardous area junction boxes lies in their construction and certification, which adhere to strict standards like ATEX and IECEx. Unlike regular junction boxes, which can be exposed to various conditions without much concern, these specialized enclosures are engineered to withstand potential explosions or fires caused by ignitable substances. This means that when asking “Which is better, Exd or Exe?”, understanding the specific requirements of your application can guide you in selecting the right type for your hazardous environment.
Key Features and Benefits
Hazardous area junction boxes boast several key features that enhance safety and reliability. They often include flameproof designs (Exd) or increased safety measures (Exe), ensuring that any internal explosion does not escape the enclosure. The benefits extend beyond mere compliance; they also reduce risks associated with maintenance and installation in potentially explosive atmospheres, making them an essential part of any electrical setup where “What are the rules for junction boxes?” must be strictly adhered to.
Common Materials Used
The materials used in constructing hazardous area junction boxes play a significant role in their effectiveness and durability. Typically made from robust substances like aluminum, stainless steel, or high-grade plastics, these materials are chosen for their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions while providing necessary protection against corrosion and impact damage. By understanding “What is the electrical code for junction boxes?”, you can ensure that the materials selected meet relevant standards while still providing optimum performance in hazardous settings.
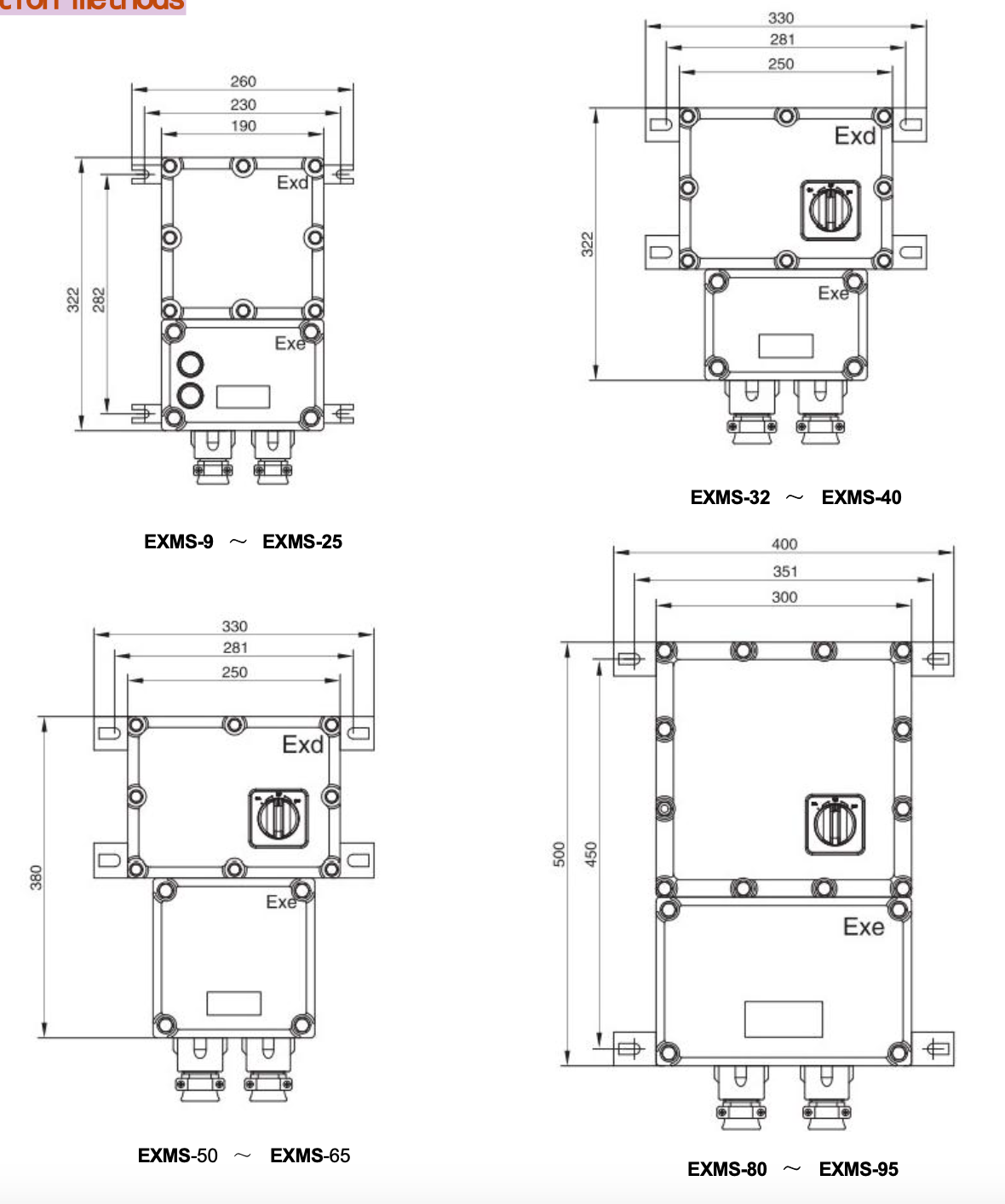
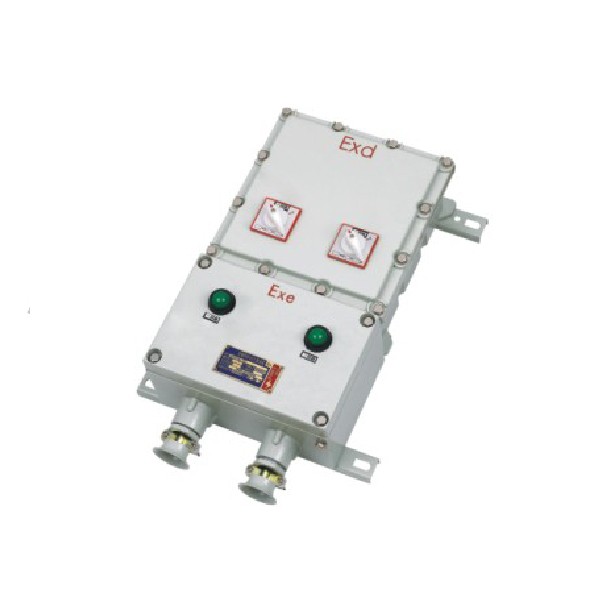
Which is Better, Exd or Exe?

When it comes to hazardous area junction boxes, the choice between Exd (flameproof) and Exe (increased safety) can feel like a high-stakes game of chess. Both types are designed to protect electrical equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres, but they do so in fundamentally different ways. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulations related to what is Zone 0 1 and 2 hazardous area classification.
Exploring Exd (Flameproof)
Exd junction boxes are built to contain any explosion that may occur within them, preventing flames from escaping into the surrounding environment. This design feature makes them particularly suitable for Zone 0 and Zone 1 areas where flammable gases or vapors are likely to be present. The robust construction of flameproof junction boxes often involves heavy-duty materials capable of withstanding significant pressure and heat, ensuring safety in hazardous conditions.
One notable characteristic of Exd junction boxes is their ability to withstand external impacts without compromising their integrity. This makes them ideal for industries such as oil and gas, where harsh environments are the norm. When considering what are the rules for junction boxes in these zones, it's essential to note that proper installation and maintenance practices will be critical for maximizing safety.
Understanding Exe (Increased Safety)
Exe junction boxes operate on a different principle; they reduce the risk of ignition by implementing increased safety measures rather than containing an explosion. These types of junction boxes prevent arcs or sparks from occurring during normal operation, making them suitable for areas classified as Zone 2 where flammable substances may occasionally be present but not constantly. The design focuses on minimizing risks through improved materials and construction techniques.
One advantage of using Exe junction boxes is their lighter weight compared to flameproof alternatives, which can make installation easier in certain applications. Additionally, they often require less stringent maintenance protocols due to their inherent safety features—making them appealing for businesses looking to streamline operations while adhering to what is the electrical code for junction boxes in hazardous areas.
Application Scenarios for Each
Choosing between Exd and Exe depends largely on the specific application scenario you’re dealing with in your industry environment. If your operations frequently involve high-risk zones like oil refineries or chemical plants, opting for flameproof structures might be your best bet—especially when dealing with Zone 0 or Zone 1 classifications where explosive atmospheres are a daily concern.
On the other hand, if you’re working in a setting such as food processing or pharmaceuticals where occasional exposure might occur but isn’t constant, you may find that increased safety solutions like Exe junction boxes fit your needs better without over-engineering your setup unnecessarily. Ultimately, understanding which type suits your operational requirements best will aid you greatly in maintaining compliance with both local regulations regarding what are the rules for junction boxes and broader electrical codes governing hazardous environments.
What are the Rules for Junction Boxes?
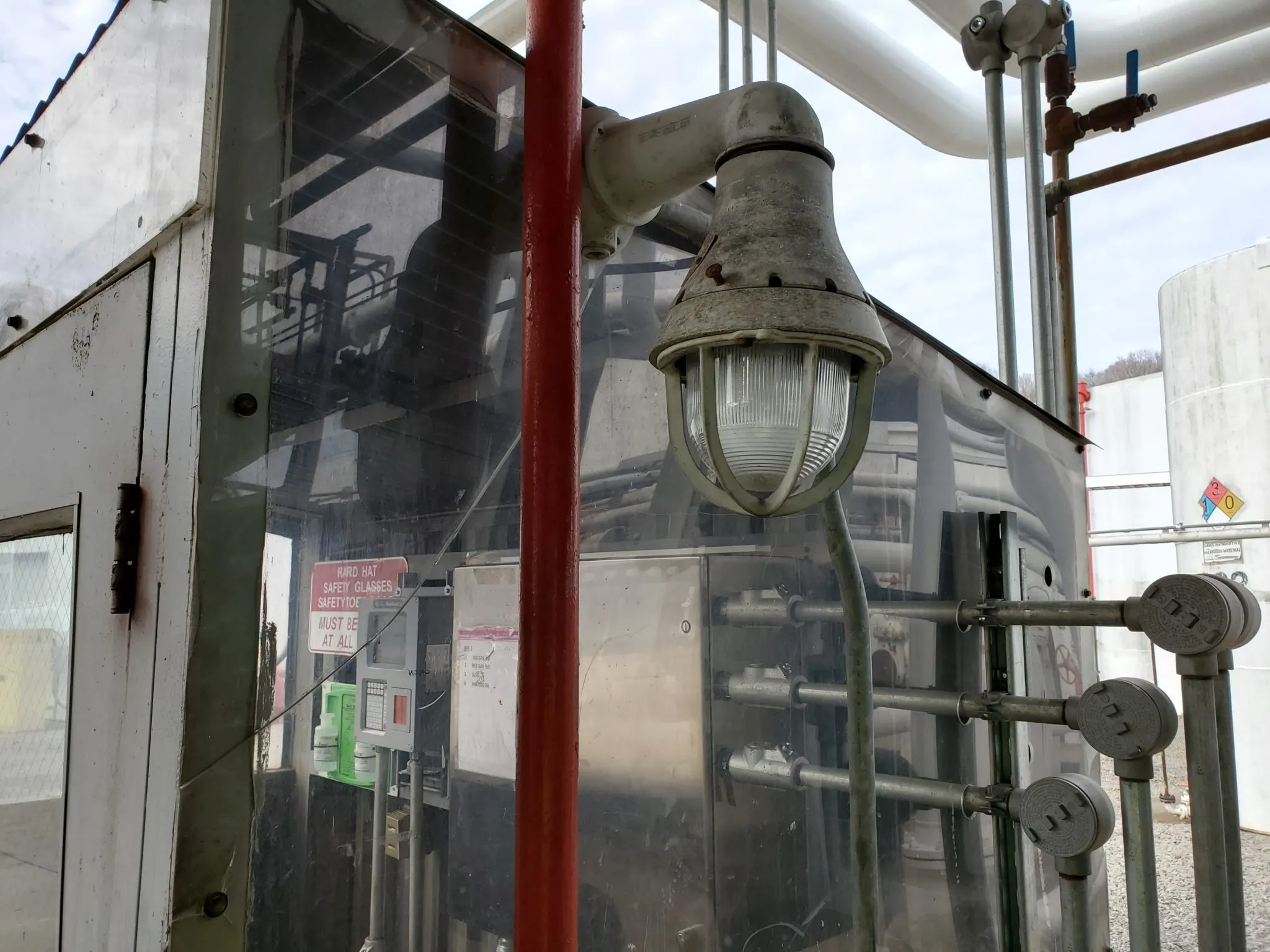

When working with hazardous area junction boxes, it's crucial to adhere to specific rules and regulations designed to ensure safety and compliance. These rules encompass a variety of electrical standards, installation guidelines, and maintenance best practices that help mitigate risks in potentially explosive environments. Ignoring these regulations can lead not only to equipment failure but also to severe safety hazards.
Key Electrical Standards
Understanding the key electrical standards is vital when dealing with hazardous area junction boxes. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the National Electrical Code (NEC) provide essential guidelines for classifying these zones and determining appropriate equipment for each classification, including what is Zone 0 1 and 2 hazardous area classification. Compliance with these standards ensures that junction boxes are suitable for their intended environments, reducing the risk of ignition sources in explosive atmospheres.
In addition to IEC and NEC guidelines, ATEX directives also play a significant role in defining requirements for hazardous areas in Europe. These directives outline necessary design features that junction boxes must have based on their intended use within different zones. Adhering to these key electrical standards not only enhances safety but also ensures that installations meet legal requirements.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation of hazardous area junction boxes is paramount for ensuring operational safety and compliance with regulations. One primary guideline is ensuring that all connections are made securely—loose wires can create sparks or short circuits leading to catastrophic failures in explosive environments. Additionally, it’s essential to follow manufacturer specifications regarding mounting locations, as improper placement can expose junction boxes to environmental factors they aren’t designed to withstand.
Another critical aspect of installation involves selecting the right type of enclosure based on its classification—this brings us back to the question: which is better, Exd or Exe? Each type has specific application scenarios where it excels; thus understanding these distinctions will guide proper installation practices tailored for your particular environment.
Lastly, it’s important not just to focus on initial installation but also on ensuring that all installed components remain accessible for future inspections or repairs without compromising safety measures.
Maintenance Best Practices
Regular maintenance of hazardous area junction boxes cannot be overstated; it’s an essential part of keeping systems safe and compliant over time. Establishing a routine inspection schedule helps identify wear-and-tear issues before they escalate into more significant problems—think loose connections or corrosion from environmental exposure! During maintenance checks, always verify that seals are intact since any breach could allow flammable gases or dust into enclosures.
In addition, cleaning procedures should be established based on the materials used in constructing your junction box; some require special solvents while others may need gentle wiping methods only! Following best practices ensures longevity while safeguarding against potential hazards associated with neglecting maintenance duties.
Finally, documenting all maintenance activities creates an invaluable record proving compliance with regulations surrounding what are the rules for junction boxes? This documentation can serve as a reference point during audits or inspections by regulatory bodies looking into adherence levels within your facility.
What is the Electrical Code for Junction Boxes?

When it comes to hazardous area junction boxes, understanding the electrical codes is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance. These codes provide guidelines that help in designing, installing, and maintaining junction boxes in environments where explosive atmospheres may exist. Familiarity with these regulations not only protects personnel but also minimizes risks associated with equipment failures.
Overview of Relevant Codes
The primary codes governing hazardous area junction boxes include the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States, as well as various international standards like IECEx and ATEX in Europe. These codes specify requirements based on the classification of zones—such as Zone 0, 1, and 2 hazardous area classification—which dictate how equipment should be designed to prevent ignition sources. Understanding these standards is essential for selecting appropriate equipment and ensuring that installations meet legal requirements.
Compliance Tips
To ensure compliance with electrical codes for junction boxes, it's vital to first identify which type of hazardous area your installation falls under—this will guide your choice between options such as Exd or Exe. Regular inspections should be part of your maintenance protocols; this includes examining seals, connections, and overall integrity to avoid potential hazards. Additionally, keeping detailed records of inspections and certifications can save you from headaches down the line when it comes time for audits or assessments.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Ignoring the electrical code for junction boxes can lead to severe consequences ranging from hefty fines to catastrophic accidents in hazardous environments. Non-compliance not only jeopardizes worker safety but could also result in significant downtime due to equipment failure or legal repercussions from regulatory bodies. Ultimately, investing time and resources into adhering to these rules pays off by safeguarding both people and property while ensuring smooth operations within industries handling volatile materials.
Conclusion

Navigating the world of hazardous area junction boxes can feel like walking through a minefield, but understanding the basics can lead you to safety and compliance. From grasping what is Zone 0, 1, and 2 hazardous area classification to deciphering whether exd or exe is better for your specific needs, knowledge is power. With the right information at your fingertips, you can ensure that your installations are safe and effective.
Summary of Hazardous Area Classifications
Hazardous area classifications are crucial in identifying environments where flammable gases or dust may be present. Specifically, what is Zone 0, 1, and 2 hazardous area classification? Zone 0 indicates areas where explosive atmospheres are continuous; Zone 1 covers areas where they are likely to occur during normal operations; and Zone 2 refers to places where such atmospheres only occasionally exist. By understanding these classifications, industries can implement suitable safety measures that protect both personnel and equipment.
Selecting the Right Junction Box
When it comes to selecting the right junction box for hazardous environments, it's essential to consider various factors including compliance with electrical codes and specific application needs. Questions like which is better, exd or exe?, often arise during this process; both have their advantages depending on the scenario at hand. Additionally, knowing what are the rules for junction boxes helps ensure that your selections adhere to necessary standards while providing optimal safety in potentially dangerous settings.
The Future of Ex-Proof Technology
Looking ahead, advancements in ex-proof technology promise even greater safety measures for hazardous area junction boxes. As industries evolve and new materials emerge, we may see enhanced designs that offer improved functionality while adhering to stringent electrical codes for junction boxes. The future holds exciting potential for innovations that not only meet current compliance requirements but also anticipate emerging challenges in hazardous environments.

