Introduction

In the world of industrial operations, understanding hazardous locations is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance. Hazardous locations refer to areas where flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or combustible dust may be present in sufficient quantities to pose a risk of fire or explosion. These environments are often classified under stringent regulations such as the NEC standards, which provide essential guidelines for safe practices and equipment selection.
What Are Hazardous Locations?
Hazardous locations are defined by their potential to contain explosive materials under certain conditions. The NEC (National Electrical Code) outlines specific classifications for these areas, known as NEC area classification charts, which categorize them based on the type of flammable materials present. Understanding where hazardous location definitions are located in the NEC is vital for professionals working in industries like oil and gas, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
Importance of NEC Standards
The importance of NEC standards cannot be overstated when it comes to safeguarding personnel and equipment in hazardous locations. These standards provide a comprehensive framework for identifying risks and implementing appropriate safety measures tailored to specific environments. Compliance with NEC 500 hazardous area classification ensures that businesses not only protect their workers but also minimize liability and operational downtime due to accidents.
Overview of Ex-Proof Equipment
Ex-proof equipment plays a pivotal role in mitigating risks associated with hazardous locations nec by preventing ignition sources from causing explosions or fires. This specialized gear is designed to withstand harsh conditions while ensuring that any potential sparks or heat generated within do not escape into the surrounding environment. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore how proper hazardous area classification can inform effective selection and use of ex-proof equipment across various industries.
The Basics of Hazardous Locations

Understanding hazardous locations is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance in industries where flammable or explosive materials are present. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides a framework for classifying these areas, detailing the risks associated with various environments. By grasping the definitions and classifications outlined in NEC standards, businesses can better navigate the complexities of hazardous area classification.
Definition and Classifications
Hazardous locations are defined as areas where there is a risk of fire or explosion due to the presence of flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or combustible dust. The NEC outlines specific classifications to help identify these locations accurately: Class I (flammable gases), Class II (combustible dusts), and Class III (ignitable fibers). Within each class, further divisions such as Division 1 and Division 2 provide additional granularity on potential hazards, making it essential to reference the NEC area classification chart when assessing a site.
Where are hazardous location definitions located in the NEC? You can find them primarily in Article 500 of the NEC, which addresses hazardous location classifications comprehensively. This article serves as a valuable resource for understanding how different environments pose varying degrees of risk and how to mitigate those risks effectively.
Common Industries Affected
Multiple industries contend with hazardous locations due to their inherent processes involving flammable materials or explosive atmospheres. Key sectors include oil and gas extraction, chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, mining operations, and food processing—each facing unique challenges related to safety protocols. Understanding these common industries affected by hazardous location classifications helps stakeholders implement tailored strategies that comply with NEC standards.
In oil refineries, for instance, volatile substances can create an environment ripe for explosions if not properly managed; hence adherence to NEC 500 hazardous area classification is paramount. Similarly, chemical plants must constantly evaluate their operations against potential hazards posed by various substances they handle daily. By recognizing which industries are impacted by hazardous locations nec regulations, companies can foster safer work environments while ensuring compliance with applicable codes.
Real-World Examples of Hazardous Locations
Real-world examples vividly illustrate the importance of understanding hazardous location classifications within different contexts. For instance, an oil drilling platform presents numerous challenges due to its exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found offshore; this necessitates strict adherence to both NEC and CE classifications for equipment used onsite. Likewise, grain silos represent another common example where combustible dust accumulation can pose significant explosion risks if not adequately monitored.
In urban settings like wastewater treatment plants, hydrogen sulfide gas generation creates a potentially lethal atmosphere if proper precautions aren’t taken; thus necessitating rigorous adherence to hazard classification guidelines outlined in the NEC standards. These examples underline why it's vital for organizations operating in such environments not only to recognize hazards but also actively engage with relevant regulations surrounding them—ensuring they’re equipped with appropriate ex-proof equipment designed specifically for these scenarios.
Navigating the NEC Standards

Understanding the National Electrical Code (NEC) is crucial for anyone involved in hazardous locations. The NEC provides guidelines that help ensure safety and compliance in environments where flammable materials may be present. By familiarizing yourself with the structure of the NEC, you can better navigate its provisions related to hazardous locations.
Understanding NEC Structure
The NEC is organized into articles, each addressing different aspects of electrical installations and safety. For hazardous locations, specific sections detail definitions, classifications, and requirements that must be adhered to when working in these potentially dangerous environments. When asking Where are hazardous location definitions located in the NEC?, you'll find them primarily within Articles 500 through 506, which provide a comprehensive framework for understanding hazardous area classification.
The structure of the NEC allows professionals to easily locate pertinent information regarding hazardous locations nec and their classifications. This organization not only aids compliance but also helps in designing safe electrical systems tailored to specific industry needs. A solid grasp of this structure will empower you to make informed decisions about equipment selection and installation practices.
Key Articles Related to Hazardous Locations
Several key articles within the NEC focus specifically on hazardous locations and their unique challenges. Article 500 outlines hazardous area classification while detailing important terms such as hazardous location classification and NEC 500 hazardous area classification. Articles 501 through 504 expand on specific areas like Class I (flammable gases), Class II (combustible dusts), and Class III (ignitable fibers), ensuring that every type of hazard is addressed appropriately.
For those looking at an overview, the NEC area classification chart serves as a handy reference tool that summarizes various classifications based on flammable materials present in different industries. Understanding these articles ensures that you are well-equipped to meet safety standards while working with Ex-proof equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres. Familiarity with these regulations can significantly reduce risks associated with electrical installations in such environments.
Compliance and Safety Considerations
Compliance with NEC standards is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a fundamental aspect of ensuring safety in hazardous locations nec. Organizations must implement thorough training programs focused on understanding both general electrical safety practices as well as specifics related to hazardous area classifications outlined by the NEC. Regular audits should also be conducted to ensure ongoing adherence to these standards.
In addition, it's crucial for companies operating in these spaces to stay updated on any changes or amendments made to the NEC over time, as regulations can evolve based on new findings or technologies introduced into the market. Ensuring compliance not only protects employees but also safeguards assets from potential hazards associated with improper equipment use or installation practices. Ultimately, embracing a proactive approach towards compliance will enhance overall safety culture within organizations operating in hazardous areas.
Types of Hazardous Locations
In the realm of hazardous locations, understanding the classifications and distinctions is key to ensuring safety and compliance with NEC standards. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides a framework for identifying hazardous areas based on the presence of flammable materials, which is crucial for selecting appropriate Ex-proof equipment. By familiarizing ourselves with these classifications, we can navigate the complexities of hazardous location definitions more effectively.
Classification by Flammable Materials
Hazardous locations are primarily classified based on the types and quantities of flammable materials present in an area. The NEC outlines specific criteria that help determine whether a location is deemed hazardous, focusing on gases, vapors, liquids, or combustible dusts. This classification system not only aids in compliance with NEC 500 hazardous area classification but also ensures that safety measures are tailored to the unique risks associated with each type of material.
For example, areas where flammable gases or vapors are present can be classified differently than those where combustible dusts accumulate. This differentiation is essential when referring to the NEC area classification chart, as it guides manufacturers and operators in selecting appropriate Ex-proof equipment designed for specific hazards. Ultimately, understanding how to classify hazardous locations by flammable materials ensures that preventative measures are in place to mitigate potential risks.
Distinction Between Zones and Classes
When discussing hazardous location classifications within the NEC framework, it's crucial to distinguish between zones and classes—two concepts that play a significant role in ensuring safety in potentially explosive environments. The NEC employs a Class/Division system primarily used in North America while other regions often utilize a Zone system aligned with international standards like IECEx and ATEX.
Classes categorize locations based on the type of hazard: Class I pertains to flammable gases or vapors; Class II refers to combustible dusts; and Class III involves ignitable fibers or flyings. On the other hand, zones offer a more detailed approach by specifying how frequently dangerous concentrations may occur—Zone 0 (continuous), Zone 1 (likely), and Zone 2 (unlikely). Understanding these distinctions not only clarifies where you can find hazardous location definitions located in the NEC but also assists professionals in determining which equipment is suitable for various scenarios.
Understanding Division and Zone Concepts
To further comprehend hazardous location classifications under the NEC guidelines, it's essential to delve into division and zone concepts that provide additional layers of specificity regarding risk assessment. In Division systems outlined by NEC regulations, Division 1 indicates areas where explosive mixtures are likely during normal operations while Division 2 covers areas where such mixtures are unlikely but could still occur under abnormal conditions.
Conversely, zone concepts categorize hazardous areas based on frequency and duration of exposure to flammable atmospheres—providing critical insights into necessary precautions when working within these environments. For instance, understanding how division and zone concepts relate helps clarify what constitutes a hazardous area classification according to both domestic regulations like those found in NEC standards as well as international frameworks like CE Classifications.
The interplay between divisions/zones plays an integral role when selecting Ex-proof equipment suited for specific applications within these defined spaces—ultimately enhancing safety protocols across various industries dealing with combustible materials regularly found at hazardous locations nec.
Selecting Ex-Proof Equipment
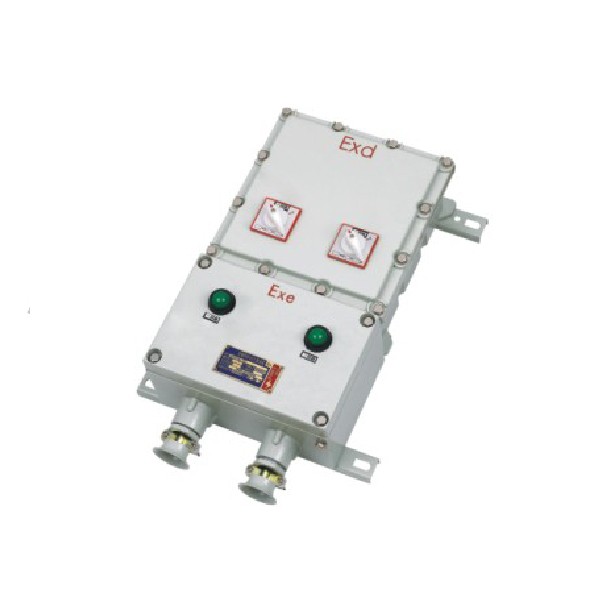

What Makes Equipment Ex-Proof?
Ex-proof equipment is engineered to contain any potential explosion within its housing, preventing it from igniting the surrounding atmosphere in hazardous locations. This design not only adheres to NEC standards but also aligns with CE classifications that ensure safety across various regions. The key features include robust materials, sealed components, and advanced technology that mitigate risks associated with volatile environments.
In addition to physical construction, ex-proof equipment must undergo rigorous testing and certification processes as outlined in NEC 500 hazardous area classification guidelines. These tests evaluate how well the equipment can withstand exposure to flammable gases or dust without compromising safety. Essentially, it's all about creating a barrier between potential hazards and operational integrity.
Key Factors in Equipment Selection
Selecting ex-proof equipment isn't as simple as picking a shiny new tool off the shelf; it requires careful consideration of several factors related to hazardous location classification. First, it’s crucial to understand the specific environment where the equipment will be used—this includes identifying the types of flammable materials present and referencing the NEC area classification chart for guidance on suitable options.
Next, compatibility with existing systems should be assessed; this means checking whether new equipment integrates seamlessly into your current infrastructure while meeting all necessary safety protocols outlined by NEC standards. Finally, maintenance requirements must also be considered—after all, even top-notch gear needs regular check-ups to ensure ongoing compliance with hazardous location definitions found within the NEC.
Jinrong’s Role in Ex-Proof Manufacturing
Jinrong has positioned itself as a leader in ex-proof manufacturing by prioritizing quality and compliance with both NEC and CE classifications for hazardous locations. Their commitment ensures that each piece of equipment not only meets but often exceeds industry standards for safety and reliability in challenging environments like oil refineries or chemical plants.
With extensive experience navigating the complexities of NEC 500 hazardous area classification, Jinrong offers a wide range of products specifically designed for diverse applications across various industries affected by hazardous locations. Their innovative solutions are backed by thorough testing processes that guarantee durability against extreme conditions while maintaining compliance with essential regulations.
By focusing on these critical aspects of selecting ex-proof equipment—understanding what makes it safe, evaluating key factors during selection, and recognizing trusted manufacturers like Jinrong—you can significantly enhance workplace safety in potentially dangerous areas.
Best Practices for Working in Hazardous Locations
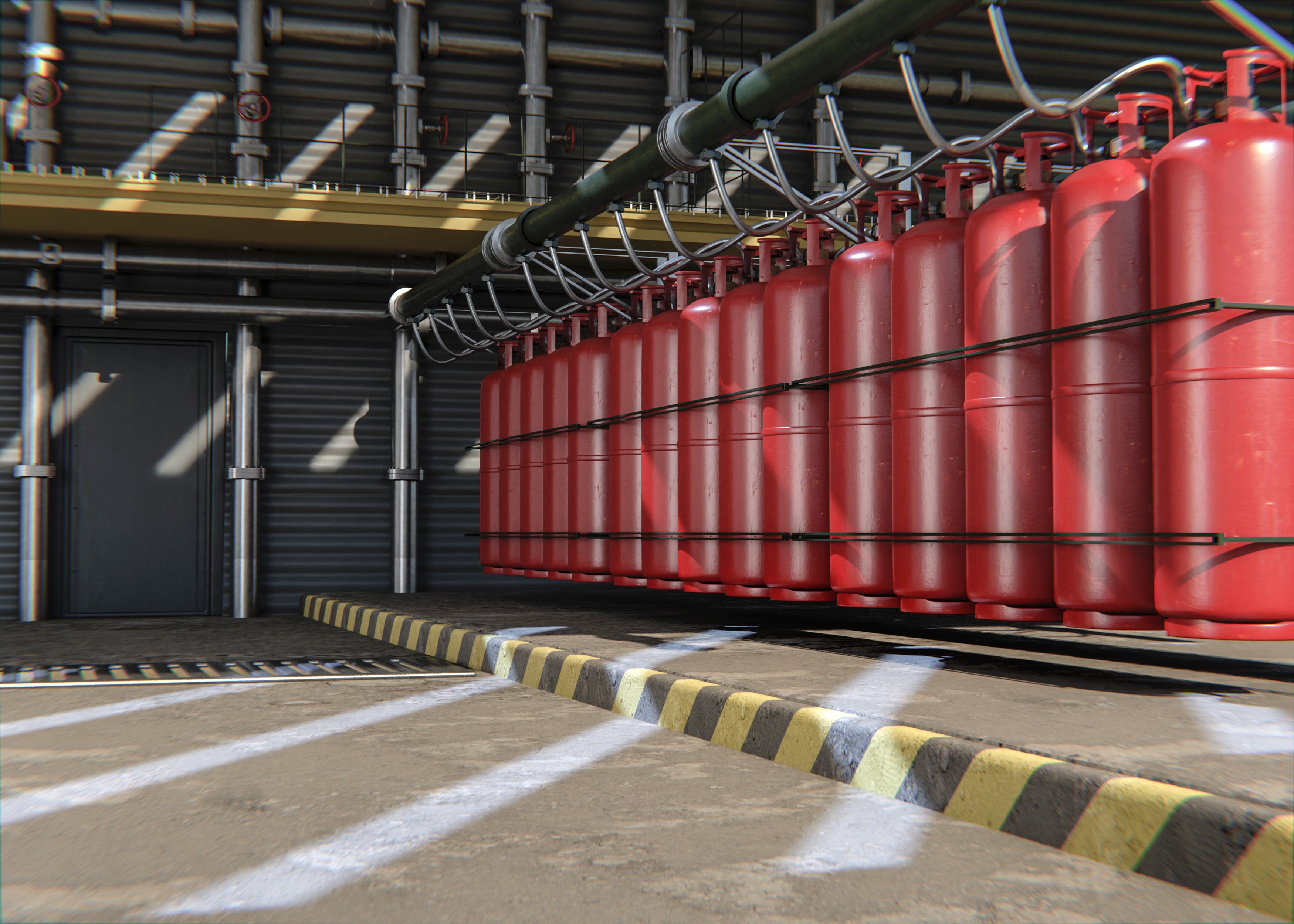

Navigating the complexities of hazardous locations requires a comprehensive approach to safety. Adhering to established protocols and procedures is essential for minimizing risks associated with flammable materials and explosive atmospheres. By understanding the NEC standards, particularly the NEC 500 hazardous area classification, workers can better protect themselves and their environments.
Safety Protocols and Procedures
When working in hazardous locations, it's crucial to implement robust safety protocols that align with NEC standards. These protocols should include clear guidelines on equipment usage, emergency response plans, and regular risk assessments tailored to specific environments. Moreover, familiarity with the NEC area classification chart helps teams identify potential hazards based on the types of flammable materials present, ensuring everyone knows how to act safely.
In addition to following established safety procedures, organizations should foster a culture of accountability where every team member feels responsible for maintaining safety standards. Regular drills that simulate emergency scenarios can also enhance preparedness among workers while reinforcing the importance of adhering to NEC classifications. Ultimately, effective safety protocols not only protect individuals but also contribute to overall operational efficiency in hazardous locations.
Training and Certification Importance
Training is paramount when it comes to ensuring personnel are equipped to handle the unique challenges posed by hazardous locations. Understanding where hazardous location definitions are located in the NEC is vital for anyone working in these environments; thus, specialized training programs focused on NEC and CE classifications are essential. Certification courses provide workers with knowledge about proper equipment handling, regulatory compliance, and emergency procedures tailored specifically for their work environments.
Moreover, ongoing education ensures that employees stay updated on any changes within NEC regulations or advancements in Ex-proof technology. This continuous learning approach empowers teams with the skills necessary to navigate complex situations confidently while fostering a safer workplace culture overall. In industries where even minor oversights can lead to catastrophic consequences, investing in training pays dividends both financially and ethically.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections play a critical role in sustaining safe operations within hazardous locations defined by NEC standards. Equipment must be routinely checked against hazard classification criteria—like those outlined in the NEC area classification chart—to ensure they remain compliant with current regulations regarding Ex-proof specifications. By conducting thorough inspections at scheduled intervals, organizations can identify potential issues before they escalate into dangerous situations.
Additionally, maintenance routines should include documenting all findings related to equipment functionality as well as adherence levels concerning hazardous location classifications set forth by the NEC guidelines. This practice not only bolsters accountability but also provides valuable data for future audits or assessments regarding workplace safety measures over time. Ultimately, regular maintenance fosters an environment of reliability while enhancing overall safety outcomes across all operations involving hazardous materials.
Conclusion

In conclusion, navigating the complexities of hazardous locations necessitates a thorough understanding of NEC standards and their implications for safety. Ensuring compliance with NEC regulations is not just a legal obligation but a vital component in safeguarding personnel and assets in potentially dangerous environments. By adhering to the NEC and CE classifications, organizations can mitigate risks associated with hazardous area classification.
Ensuring Compliance with NEC
Compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) is paramount when working in hazardous locations. The NEC 500 hazardous area classification provides essential guidelines that help identify and manage risks related to flammable materials. Understanding where hazardous location definitions are located in the NEC allows professionals to implement appropriate safety measures effectively, ensuring that all equipment meets necessary standards.
Regular training on the latest NEC area classification chart is crucial for maintaining compliance and enhancing workplace safety. This knowledge empowers workers to recognize potential hazards and respond appropriately, minimizing accidents in these environments. Moreover, staying updated on any changes or revisions to the NEC ensures ongoing compliance and protection against liability issues.
Enhancing Safety in Hazardous Locations
Enhancing safety in hazardous locations requires a multifaceted approach that combines proper equipment selection, rigorous training, and strict adherence to established protocols. By implementing best practices based on recognized standards like those found within the NEC framework, organizations can create safer work environments for their employees. Regular maintenance checks also play a critical role in ensuring that equipment remains functional and safe over time.
Training staff on how to navigate hazardous location classifications fosters an environment of awareness and preparedness among workers. It's essential for employees to understand both the risks involved and how to utilize ex-proof equipment correctly within these settings. By prioritizing education around hazardous location definitions from the NEC, companies can cultivate a culture of safety that extends beyond mere compliance.
The Future of Ex-Proof Equipment
The future of ex-proof equipment looks promising as technology continues to evolve alongside industry needs for enhanced safety solutions in hazardous locations. Innovations are being made not only in design but also in materials used for manufacturing ex-proof devices—ensuring they meet stringent standards while remaining user-friendly. As industries become more aware of the importance of proper hazard management through NEC guidelines, we can expect an increase in demand for cutting-edge ex-proof solutions.
Furthermore, advancements such as smart technology integration will likely transform how we approach monitoring conditions within hazardous areas classified by the NEC area classification chart. This evolution could lead to real-time data collection that informs better decision-making regarding safety measures and equipment usage. Ultimately, embracing these technological developments will enable organizations to enhance their operational efficiency while prioritizing employee safety within potentially dangerous environments.

