Introduction
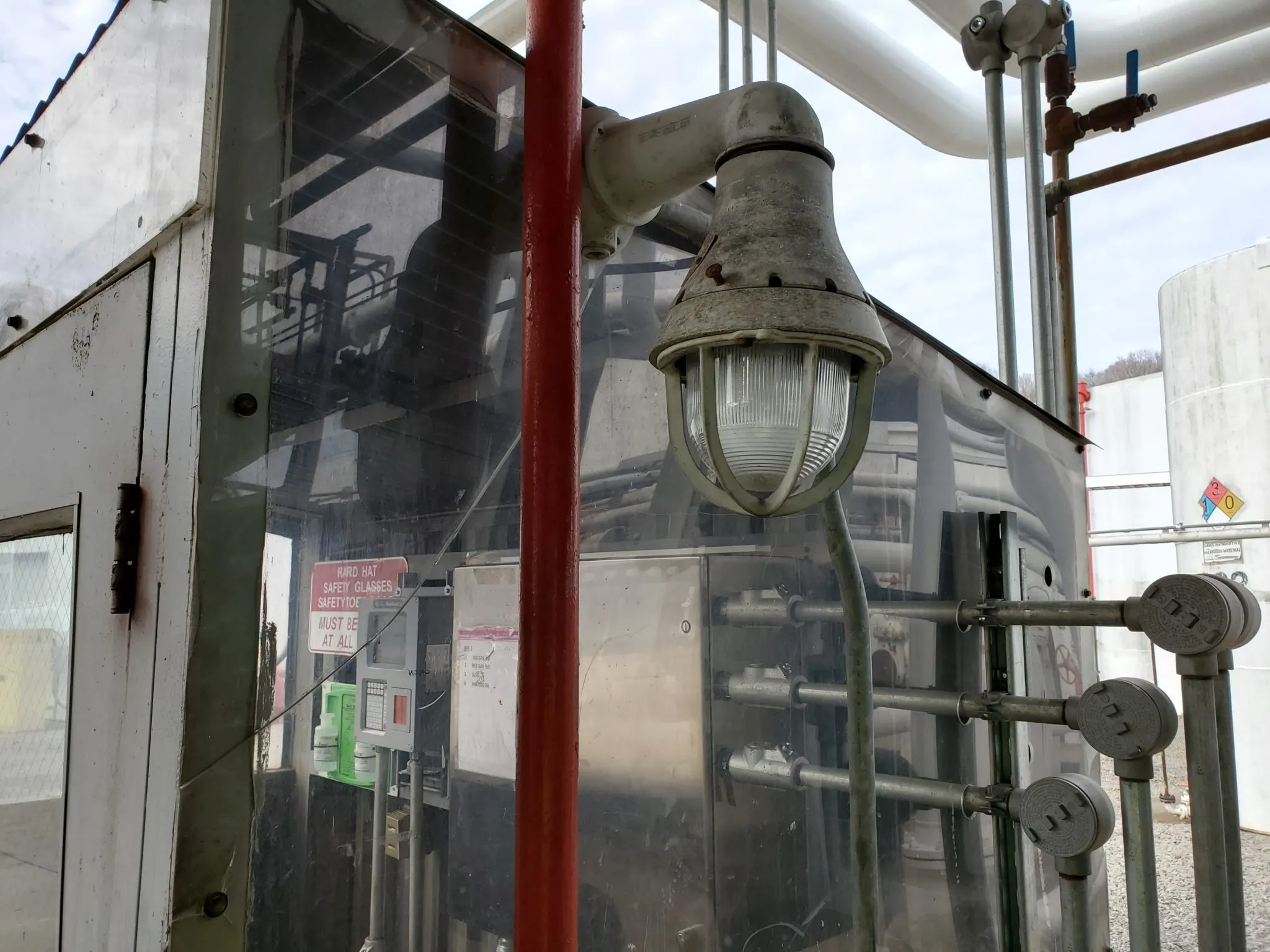

In today's industrial landscape, understanding hazardous environments is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance. With the potential for explosive atmospheres in various sectors, it becomes imperative to differentiate between technologies designed to mitigate these risks. This is where the concepts of non-incendive vs intrinsically safe come into play, each offering unique safety features tailored to specific applications.
Understanding Hazardous Environments
Hazardous environments can be found in industries such as oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and mining, where flammable gases or dust are prevalent. In such settings, equipment must be designed to prevent ignition sources that could lead to catastrophic incidents. Familiarity with terms like non-incendive meaning and what qualifies as intrinsically safe is essential for professionals working in these fields.
Importance of Safety Standards
Safety standards serve as a framework for ensuring that equipment operates safely in hazardous conditions. They help define the parameters under which devices can be classified as non-incendive or intrinsically safe, ultimately guiding manufacturers and users alike in their choices. By adhering to these standards, organizations not only protect their workers but also minimize liability and enhance operational efficiency.
Overview of Non Incendive and Intrinsically Safe
Non-incendive circuits are designed so that any electrical sparks or heat generated during normal operation cannot ignite a surrounding explosive atmosphere. Conversely, intrinsically safe equipment is engineered with even stricter controls that limit energy levels to prevent ignition under fault conditions. Understanding the nuances between non-incendive vs explosion proof further enriches our comprehension of safety solutions available today.
What Defines Non Incendive?

In the realm of hazardous environments, understanding what defines non incendive technology is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance. Non incendive equipment is designed to operate without producing sparks or excessive heat that could ignite flammable substances in the surrounding atmosphere. This means that while non incendive circuits are not entirely foolproof, they provide a level of protection that makes them suitable for specific applications, particularly when compared to other safety standards like intrinsically safe or explosion-proof designs.
Non Incendive Meaning in Practice
The term non incendive refers to devices or circuits that are engineered to minimize the risk of ignition in potentially explosive atmospheres. In practice, this means that these systems can safely operate under conditions where flammable gases or vapors may be present, as long as they remain within certain parameters such as voltage and current limits. It’s important to note that non incendive does not equate to being “intrinsically safe”; rather, it indicates a different approach to managing risk—one which focuses on preventing ignition sources during normal operation.
Examples of Non Incendive Circuits
A classic example of a non-incendive circuit can be found in certain types of control systems used in industrial settings. For instance, a simple relay circuit designed for use with sensors in a chemical processing plant may qualify as non incendive if it operates below specified energy levels and does not produce sparks during normal functioning. Other examples include signal transmission lines and low-power communication devices that adhere to non-incendive standards; these components play an essential role in ensuring operations run smoothly without compromising safety.
Applications of Non Incendive Technology
Non incendiary technology finds its niche primarily in industries such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing where explosive atmospheres are common. For instance, using non-incendive circuits for monitoring equipment allows operators to maintain oversight without introducing additional hazards into their environments. Furthermore, this technology also supports various applications like process automation and remote sensing—demonstrating its versatility while maintaining compliance with safety regulations.
Exploring Intrinsically Safe Standards

What Qualifies as Intrinsically Safe?
To determine if a device is intrinsically safe, it must be designed in such a way that any spark or thermal effect produced under normal operation cannot ignite a hazardous atmosphere. This involves rigorous testing and certification processes that assess energy levels, temperature, and other factors. In contrast to non incendive systems, which limit energy but may still pose risks under fault conditions, intrinsically safe devices provide an added layer of protection in volatile environments.
Key Intrinsically Safe Devices
There are several key devices that fall under the category of intrinsically safe equipment. Common examples include sensors, transmitters, and communication devices designed for use in explosive atmospheres like oil rigs or chemical plants. Understanding the differences between these devices and their non incendive counterparts can help organizations choose the right tools for their specific applications.
Benefits of Intrinsically Safe Equipment
The benefits of using intrinsically safe equipment are numerous and significant. First, they enhance workplace safety by minimizing risks associated with explosions in hazardous areas—something every organization strives for! Additionally, they often require less maintenance compared to explosion-proof equipment due to their lower operational temperatures and reduced wear-and-tear from excessive heat generation. Ultimately, investing in intrinsically safe technology can lead to long-term cost savings while ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Non Incendive vs Intrinsically Safe

When navigating the complexities of safety in hazardous environments, understanding the differences between non-incendive and intrinsically safe technologies is crucial. While both aim to prevent ignition sources in potentially explosive atmospheres, they do so through different methodologies and standards. This section delves into the nuances of these two approaches, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications.
Is Non-Incendive the Same as Intrinsically Safe?
The short answer is no; non-incendive is not the same as intrinsically safe. Non-incendive circuits are designed to limit energy levels to a point where ignition cannot occur under normal conditions, but they may not provide protection in fault conditions. In contrast, intrinsically safe devices are engineered to prevent any possibility of ignition even during faults by ensuring that energy levels remain below a threshold that could ignite a hazardous atmosphere. Understanding this distinction—non-incendive vs intrinsically safe—can significantly impact safety decisions in industrial settings.
Comparing Safety Ratings and Applications
When it comes to safety ratings, non-incendive systems typically fall under less stringent regulations compared to intrinsically safe devices. The latter often requires rigorous testing and certification processes due to their critical role in safeguarding against explosions in volatile environments. For example, while non-incendive applications might be suitable for certain manufacturing areas with limited risk factors, intrinsically safe equipment is essential for industries like oil and gas or chemical processing where risks are considerably higher.
Real World Examples and Use Cases
In practical terms, consider a factory setting where machinery operates near flammable materials; here, non-incendive circuits might be employed effectively without raising alarms about potential hazards. On the other hand, an oil rig operating under extreme conditions would necessitate intrinsically safe equipment due to its heightened risk profile—where even a small spark could lead to catastrophic results. By examining these real-world examples of non-incendive vs intrinsically safe technologies, we gain valuable insights into how different applications dictate the choice between these two safety solutions.
Non Incendive vs Explosion Proof

When it comes to ensuring safety in hazardous environments, understanding the difference between non incendive and explosion-proof technologies is crucial. Both approaches aim to prevent ignition sources, but they do so through different methodologies and applications. This section will clarify these distinctions and help you navigate the complexities of these safety standards.
What is the Difference Between Intrinsically Safe and Explosion-Proof?
To understand non incendive vs intrinsically safe, we first need to clarify what qualifies as intrinsically safe. Intrinsically safe devices are designed to limit energy levels—both electrical and thermal—so that they cannot ignite flammable materials, even under fault conditions. On the other hand, explosion-proof equipment is built to contain an explosion within its enclosure; it prevents any internal ignition from escaping into the surrounding area.
So, what is the difference between intrinsically safe and explosion-proof? While both aim to mitigate risks associated with hazardous environments, their methods diverge significantly: intrinsically safe designs focus on energy limitation while explosion-proof solutions emphasize containment. This fundamental distinction leads us into a deeper exploration of their respective applications and effectiveness in various scenarios.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that can influence your choice based on project requirements. Non-incendive circuits offer simplicity in design and installation since they don’t require heavy enclosures or special housing; however, they may not be suitable for all environments due to their limited energy control capabilities. Meanwhile, while explosion-proof systems provide robust protection against potential explosions by containing them effectively, they can be more expensive due to their complex construction requirements.
In terms of maintenance, non-incendive technology often requires less upkeep compared to explosion-proof setups that may need regular inspections for wear or damage due to their more intricate designs. However, one must consider whether a non-incendive circuit will suffice for specific hazards present in a work environment where flammable gases or dust are prevalent. Ultimately, weighing these pros and cons will guide you toward making an informed decision about which method aligns best with your project's needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing between non incendive vs explosion proof solutions involves assessing several factors unique to your project’s environment and safety requirements. Start by evaluating the nature of potential hazards—if highly volatile substances are present, an intrinsically safe device might be necessary for compliance with safety regulations. Conversely, if containment is paramount due to high-pressure situations or larger volumes of flammable materials, then opting for an explosion-proof system could be wiser.
Additionally, consider installation costs versus operational efficiency; while initial expenses might differ significantly between these two approaches (with non-incendive circuits generally being less costly), long-term maintenance should also factor into your decision-making process. Understanding what qualifies as intrinsically safe versus how well an explosion-proof system performs under specific conditions will ultimately drive you toward making the right choice tailored specifically for your project needs.
Jinrong’s Expertise in Hazardous Area Solutions
In an industry where safety is paramount, Jinrong stands out as a leader in providing innovative solutions for hazardous environments. Our commitment to excellence is reflected in our advanced non incendive and intrinsically safe products, designed to meet stringent safety standards while enhancing operational efficiency. With a deep understanding of the nuances between non incendive vs intrinsically safe technologies, we ensure that our offerings not only comply with regulations but also exceed customer expectations.
Innovations in Non Incendive and Intrinsically Safe Products
At Jinrong, we recognize the importance of innovation in developing non incendive circuits that cater to diverse applications. Our research and development team continuously explores cutting-edge technologies to enhance the safety and reliability of our products, ensuring they meet the rigorous qualifications needed for intrinsically safe certification. By integrating smart technology into our designs, we provide solutions that not only mitigate risks associated with hazardous environments but also improve overall performance.
When it comes to understanding what qualifies as intrinsically safe, our products exemplify this standard through their meticulous design and testing processes. We have developed a range of devices that demonstrate how non incendive meaning translates into practical applications across various industries, from oil and gas to pharmaceuticals. By investing in innovation, we empower businesses to operate safely without compromising on productivity or efficiency.
Supporting Distributors with Quality Equipment
Jinrong takes pride in supporting distributors by providing high-quality equipment tailored for hazardous areas. Our comprehensive product line includes both non incendive and intrinsically safe devices that are essential for ensuring workplace safety. Understanding the difference between intrinsically safe and explosion-proof equipment allows us to guide distributors effectively in selecting the right solutions for their clients' specific needs.
Moreover, by offering extensive training resources and technical support, we enable our distributors to confidently promote our products while addressing any questions about non-incendive vs explosion proof technologies. This collaborative approach ensures that end-users receive informed recommendations based on their unique requirements while maintaining compliance with safety standards. Ultimately, our goal is to equip distributors with everything they need to succeed in delivering top-notch hazardous area solutions.
Our Commitment to Safety and Compliance
Safety isn't just a checkbox for us; it's woven into the fabric of everything we do at Jinrong. We understand that choosing between non-incendive vs intrinsically safe options can be daunting; therefore, we prioritize clear communication about what distinguishes these technologies from one another. Our commitment extends beyond product development—ensuring compliance with international standards is integral to maintaining trust within the industry.
We actively participate in industry forums and contribute towards setting benchmarks that govern what constitutes a reliable non-incendive circuit or an effective explosion-proof solution. This proactive stance keeps us ahead of emerging trends while reinforcing our dedication to fostering safer working environments everywhere we operate. As we look toward the future of safety in hazardous areas, Jinrong remains resolute in its mission: providing unparalleled expertise backed by innovative solutions tailored for every challenge.
Conclusion

In the realm of hazardous environments, understanding the distinctions between non incendive and intrinsically safe technologies is crucial for ensuring safety. Non incendive circuits operate under specific conditions that prevent ignition in potentially explosive atmospheres, while intrinsically safe devices are designed to eliminate any chance of ignition altogether. By grasping these concepts, one can make informed decisions about which safety measures to implement.
Key Takeaways on Non Incendive and Intrinsically Safe
To summarize, non incendive technology allows for limited energy transfer that mitigates explosion risks, while intrinsic safety focuses on preventing any electrical energy from causing ignition in hazardous areas. The question often arises: Is non-incendive the same as intrinsically safe? The answer lies in their operational principles; while both aim to enhance safety in explosive environments, they do so through different methodologies and standards. Understanding what qualifies as intrinsically safe or recognizing a non-incendive circuit can significantly impact safety protocols across various industries.
Importance of Choosing the Right Equipment
Selecting the appropriate equipment for hazardous environments is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a matter of life and death. Whether you’re deciding between non-incendive vs explosion proof solutions or weighing the pros and cons of each approach, your choice should reflect both safety needs and operational efficiency. The difference between intrinsically safe and explosion-proof designs can influence everything from installation costs to maintenance requirements—making informed decisions imperative for optimal performance.
Future of Safety in Hazardous Environments
Looking ahead, advancements in technology will likely continue to enhance our understanding and implementation of safety standards like those governing non incendive vs intrinsically safe equipment. As industries evolve, so too will the strategies for mitigating risks associated with hazardous environments—ensuring that innovations keep pace with emerging challenges. Ultimately, fostering a culture that prioritizes safety will lead us toward a more secure future where accidents are minimized through intelligent design choices.

