Introduction

Understanding hazardous materials is crucial for ensuring safety in transportation and manufacturing. Hazmat materials encompass a wide range of substances that pose potential risks to health, safety, and the environment. Based on their characteristics and potential hazards, these materials are classified into different hazard classes, including flammable and non-flammable gases. Hazmat placards play a vital role in identifying these materials during transportation and are essential for ensuring proper handling and emergency response.
Understanding Hazardous Materials
Understanding hazardous materials is essential for anyone involved in their transportation, storage, or use. These materials encompass a wide range of substances that can cause harm to people, property, or the environment. From corrosive liquids to explosive chemicals, hazmat materials require special handling to prevent accidents and minimize risks.
Hazmat Classifications
Hazmat classifications categorize hazardous materials based on their physical and chemical properties. This classification system helps identify the potential hazards associated with each material and determines the appropriate safety measures for handling them. One such hazard class includes flammable and non-flammable gases, requiring specific precautions due to their unique characteristics.
Hazmat classifications are essential for safe handling and transportation of hazardous materials. By categorizing these materials based on their properties, such as flammability, toxicity, or reactivity, it becomes easier to assess the potential risks involved. For example, flammable and non-flammable gases present different challenges regarding containment and storage, making it crucial to have specific safety measures for each type. This classification system helps identify hazards and guides emergency responders in effectively managing incidents involving hazardous materials.
Importance of Hazmat Placards
Hazmat placards are essential visual indicators used in the transportation of hazardous materials. They provide vital information to emergency responders and others about the potential risks associated with the cargo.
- Standardized Format: Hazmat placards display hazard class information in a standardized format, ensuring quick and easy identification.
- Regulatory Requirement: Proper display of hazmat placards is an essential regulatory requirement for public safety.
- Communication Tool: Hazmat placards serve as a valuable communication tool for first responders, allowing them to assess the situation and determine appropriate actions.
- Public Safety: By providing clear and concise information, hazmat placards help prevent accidents and minimize the impact of incidents, safeguarding public safety.
The proper use and display of hazmat placards are crucial for ensuring the safe transportation of hazardous materials and protecting the public.
Classifying Flammable and Non-Flammable Gases

When it comes to hazardous materials, Class 2 includes both flammable and non-flammable gases, making it a diverse category. Flammable gases such as propane and butane fall under Class 2.1, while non-flammable gases like nitrogen and helium are categorized as Class 2.2. Understanding the unique properties of each type is important to ensure safe handling.
Identifying Class 2 Hazardous Materials
Class 2 hazardous materials are easily recognizable by their hazmat placards, which display the specific hazard class of the transported material. These placards are crucial for identifying the contents of a shipment and alerting emergency responders in the event of an accident. Understanding the different classifications within Class 2 is essential for proper handling.
Knowing the different classifications within Class 2 hazardous materials is important when handling them. For example, flammable gases are one type of Class 2 material that requires special precautions due to their explosive nature. Understanding the hazards associated with flammable gases can help ensure proper safety measures are in place for handling and transporting these materials. By being knowledgeable about the characteristics of flammable gases, individuals can minimize the risk of accidents and protect themselves and others from potential harm.
Safety Measures for Handling Flammable Gases
When dealing with flammable gases, safety measures must be strictly adhered to to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of individuals and property. This includes proper storage, transportation, handling procedures, and using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with these materials. It is important to conduct regular inspections and equipment maintenance to ensure it is in good working condition, as any malfunction could lead to a potential hazard. Additionally, all personnel should be properly trained in safely handling flammable gases and be aware of emergency procedures in case of a spill or leak.
Risks Associated with Non-Flammable Gases
While non-flammable gases might not ignite, they still pose significant safety hazards. Here are some key risks to be aware of:
- Asphyxiation: Some non-flammable gases, like carbon dioxide and nitrogen, can displace oxygen in enclosed spaces, leading to suffocation.
- Extreme Temperatures: Cryogenic gases like liquid nitrogen and argon can cause severe burns upon contact due to their extremely cold temperatures.
- Overpressurization: Improper storage or handling of non-flammable gases in sealed containers can lead to excessive pressure buildup, potentially resulting in explosions.
To ensure safety when working with non-flammable gases, always follow proper storage and handling procedures, provide adequate ventilation, and be aware of the hazards associated with each gas.
Hazmat Placards for Gases

Hazmat placards are crucial in identifying the type of hazardous materials being transported. Regarding gases, differentiating hazard class placards is essential for ensuring proper handling and safety measures. Class 2 is the hazard class that includes both flammable and non-flammable gases, making it important to differentiate between the two accurately.
Differentiating Hazard Class Placards
Differentiating hazard class placards for gases involves understanding the specific characteristics of each type of gas. For example, flammable gases such as methane or propane require a different placard than non-flammable gases like nitrogen or helium. Proper identification ensures that appropriate safety measures are implemented during transportation and handling.
Proper identification of hazard class placards is crucial for the safety of the individuals handling the gases and the general public. Understanding the specific characteristics of each gas type allows for the implementation of appropriate safety measures during transportation and handling. This includes using the correct placard to alert emergency responders and others to the potential hazards associated with a particular type of gas, ensuring that everyone knows how to respond in case of an accident.
Significance of Proper Placarding
Proper placarding is significant in preventing accidents and ensuring the safety of all individuals involved in transporting and handling hazardous materials. It allows for quick identification of the potential risks associated with specific hazmat materials, enabling responders to take necessary precautions in an emergency.
Proper placarding also helps in the proper segregation of different hazardous materials during transportation and storage. This ensures that incompatible substances are not placed together, reducing the risk of chemical reactions or spills that could lead to accidents or environmental contamination. By clearly indicating the nature of the materials being transported, placarding also helps minimize the potential for human error in handling these substances.
Regulatory Requirements for Placarding
The safe transportation of hazardous materials is a critical aspect of modern logistics. Regulatory bodies have established guidelines for placarding vehicles carrying these substances to minimize risks and protect public safety. One such agency is the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States, which sets specific requirements for displaying hazard class placards.
- Placarding Requirements: The DOT mandates using hazard class placards on vehicles transporting hazardous materials, including gases. These placards warn others about the potential dangers associated with the cargo.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to DOT regulations is essential to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with safety standards. Failure to comply can result in severe consequences, including fines and legal action.
- Hazard Class Differentiation: Proper differentiation of hazard class placards is crucial for effective communication and emergency response. Each hazard class has a unique placard design and color code identifying the specific type of hazardous material being transported.
- Staying Informed: Individuals and organizations involved in transporting hazardous materials must stay updated on the latest regulatory requirements for placarding. This includes understanding any changes or updates to existing guidelines and ensuring compliance with the specific placarding requirements for different hazardous materials.
By understanding the importance of properly differentiating hazard class placards, acknowledging their significance in ensuring safety, and complying with regulatory requirements, individuals can effectively navigate hazmat transportation and handling processes while prioritizing safety at all times. Staying informed about DOT regulations and implementing proper placarding practices is essential for protecting public health and minimizing the risks associated with hazardous materials transportation.
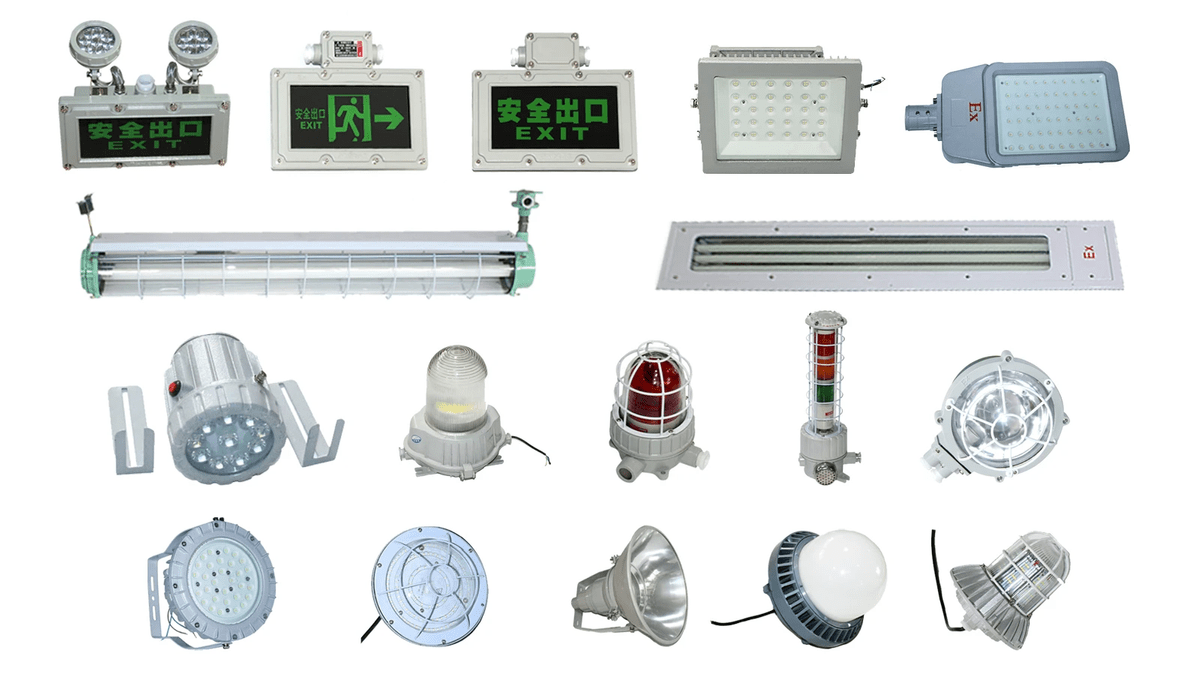
Ex-Proof Manufacturing and Hazmat Materials

Ex-proof equipment is crucial in hazardous environments where flammable gases pose a significant risk. These specialized devices are designed to prevent the ignition of hazardous materials, making them essential for maintaining safety in such volatile settings.
Importance of Ex-Proof Equipment in Hazardous Environments
In environments where hazardous materials are present, using ex-proof equipment is vital for ensuring the safety of personnel and facilities. These specialized devices are engineered to prevent sparks and heat from igniting flammable gases, reducing the risk of explosions and fires in these high-risk areas.
Ex-proof equipment is crucial for the safety of personnel and facilities and for maintaining regulatory compliance in hazardous environments. Companies can demonstrate their commitment to upholding safety standards and protecting their workers by using certified ex-proof lighting series. Additionally, these specialized devices can help reduce insurance premiums by minimizing the risk of accidents and property damage, making them a cost-effective investment for businesses operating in high-risk areas.
Certifications for Ex-Proof Lighting Series
The certifications for the ex-proof lighting series play a critical role in guaranteeing their suitability for use in hazardous locations. These certifications ensure that the lighting fixtures meet stringent safety standards and can withstand potential hazards, providing peace of mind to those working in these environments.
The certifications for ex-proof lighting series are critical in guaranteeing their suitability for use in hazardous locations. These certifications ensure that the lighting fixtures meet stringent safety standards and can withstand potential hazards, providing peace of mind to those working in these environments. In addition to meeting safety standards, these certifications demonstrate compliance with industry regulations, giving users confidence that they are investing in reliable and legally approved lighting solutions. Furthermore, having these certifications can streamline the approval process for installation in hazardous locations, saving time and resources for businesses.
Ensuring Safety with Ex-Proof Accessories
In addition to lighting fixtures, ex-proof accessories such as switches, sockets, and control panels also play a crucial role in maintaining safety in hazardous environments. These accessories are designed to minimize the risk of ignition, offering an extra layer of protection against potential hazards associated with class 9 hazardous materials. By incorporating these ex-proof accessories into the design and operation of facilities handling hazardous materials, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to safety and regulatory compliance. Using ex-proof accessories can also help reduce insurance premiums by showcasing a proactive approach to risk management and workplace safety.
By prioritizing the use of ex-proof equipment and accessories, businesses can effectively mitigate the risks of handling class 9 hazardous materials while maintaining a safe working environment for their employees.
Hazmat Handling Best Practices

When it comes to the safe transportation of Class 9 hazardous materials, strict guidelines must be followed to prevent accidents and protect the environment. Proper packaging, labeling, and securing of the materials are essential to ensure they arrive at their destination without incident. Additionally, drivers should be well-trained in handling these materials and equipped with emergency response plans in case of any unforeseen events.
Safe Transportation of Class 9 Hazardous Materials
Class 2 is the hazard class that includes both flammable and non-flammable gases. When transporting these hazardous materials, it's important to use specialized containers to withstand the pressure and temperature changes that may occur during transit. Proper ventilation and segregation from other incompatible substances are also critical to minimize the risk of accidents or leaks during transportation.
Guidelines for Handling Hazmat Materials
Handling hazmat materials requires strict adherence to guidelines set forth by regulatory agencies such as the Department of Transportation (DOT) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). This includes proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures to mitigate potential risks of these hazardous substances. Regular equipment inspections and maintenance are also necessary to ensure safe handling practices.
Employee Training and Compliance
Employee training is vital in ensuring compliance with hazmat regulations. Workers involved in handling hazardous materials must undergo thorough training on proper protocols for storage, transportation, and emergency response procedures. Regular refresher courses should be provided to keep employees up-to-date on the latest safety measures and regulatory requirements.
Prioritize Safety in Hazmat Handling
In conclusion, prioritizing safety in hazmat handling is crucial to preventing accidents and protecting the environment. Partnering with reliable distributors ensures access to high-quality hazmat materials and placards. Continuous innovation in ex-proof manufacturing allows for the development of safer equipment for hazardous environments.
Safety should always be the top priority when handling hazardous materials, especially class 9 hazardous materials. Proper training and compliance with regulations are essential to minimize risks and ensure the well-being of employees and the community.
Partnering with Reliable Distributors
Choosing trustworthy distributors for hazmat materials is key to guaranteeing the quality and reliability of your products. By partnering with reputable suppliers, you can have peace of mind knowing that you are obtaining materials that meet safety standards and regulations.
Continuous Innovation in Ex-Proof Manufacturing
Continuous innovation in ex-proof manufacturing is essential for creating safer equipment for hazardous environments, including those that handle flammable and non-flammable gases. Manufacturers can develop cutting-edge solutions that enhance safety and efficiency by investing in advanced technology and research.
Remember, when it comes to hazmat handling, prioritizing safety, working with reliable distributors, and embracing innovation are all crucial elements for success.

