Introduction
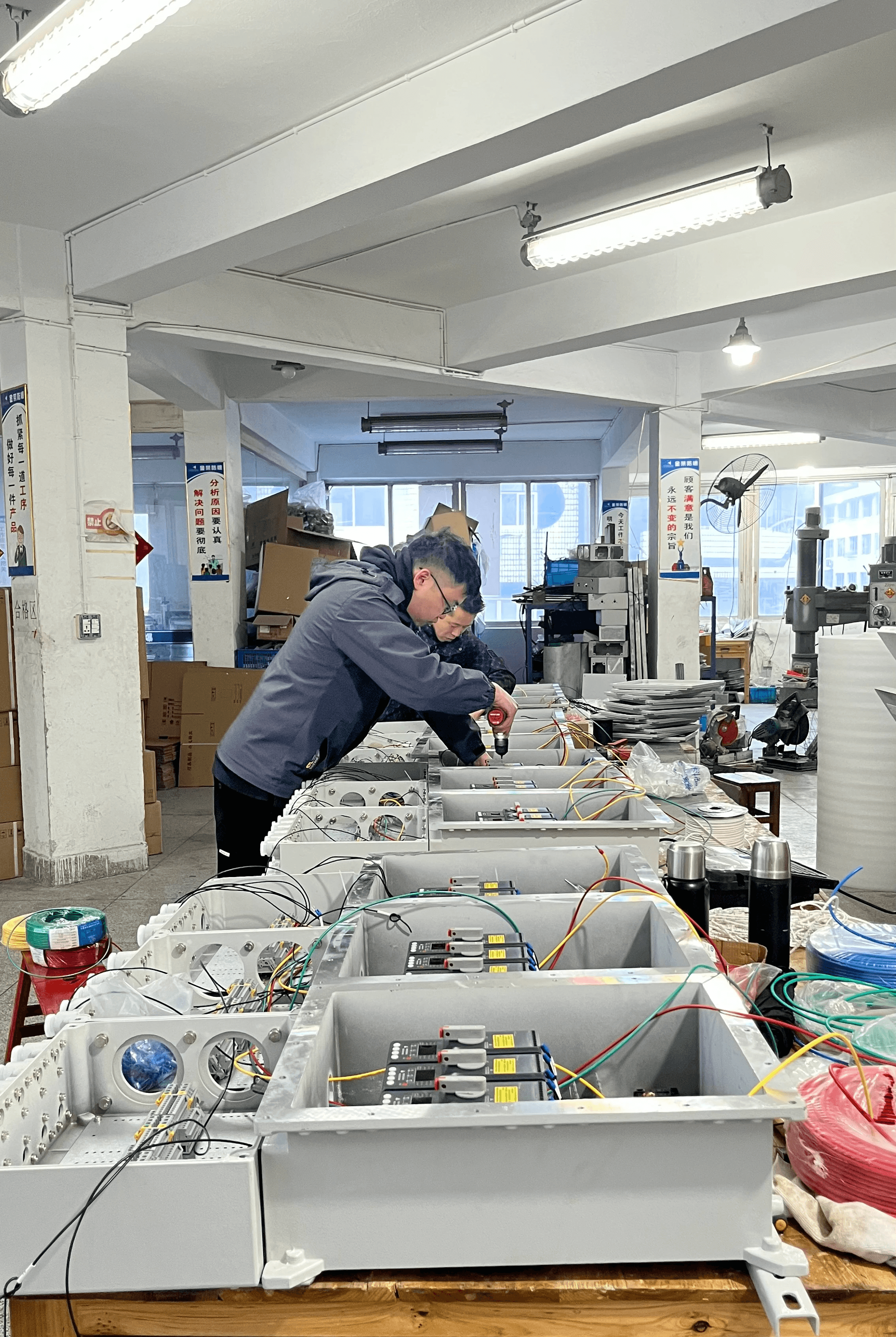
In today’s fast-paced industrial world, understanding intrinsically safe requirements is not just a matter of compliance; it’s essential for ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment in hazardous environments. With the ever-present risk of explosions or electrical failures, adhering to stringent electrical safety standards becomes paramount. This is where the ATEX certification plays a crucial role, acting as a beacon of safety that guides organizations toward best practices in intrinsic safety.
Understanding Intrinsically Safe Requirements
Intrinsically safe requirements are designed to prevent ignition hazards in environments where flammable gases or dust may be present. These principles dictate how electrical devices should be constructed and operated to minimize risks, particularly in Class 1 Division 1 locations. By focusing on essential elements like cables wiring and electrical panel wiring, organizations can ensure that their equipment meets the necessary standards for safe operation.
Importance of Electrical Safety Standards
Electrical safety standards serve as the backbone of any effective safety strategy in industries dealing with hazardous materials. They provide guidelines that help manufacturers and operators understand how to design systems that comply with intrinsic safety principles, thus reducing potential risks significantly. Without these standards, organizations would be navigating a treacherous landscape fraught with dangers that could lead to catastrophic outcomes.
The Role of ATEX Certification in Safety
The ATEX standard is vital for ensuring that equipment used in explosive atmospheres meets rigorous safety criteria. This certification not only confirms compliance with intrinsic safety regulations but also enhances trust among stakeholders regarding operational integrity. By aligning with ATEX certification requirements, companies demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high levels of safety while optimizing their processes for efficiency.
What are Intrinsically Safe Requirements?
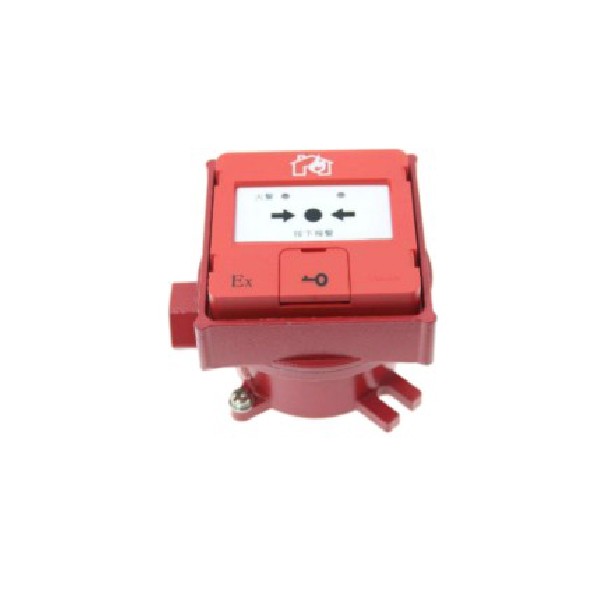

Understanding intrinsically safe requirements is essential for ensuring safety in environments where flammable gases, vapors, or dust exist. At its core, intrinsic safety is a protection technique that limits the energy available for ignition in hazardous locations, making it a critical aspect of electrical design. By adhering to these principles, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of explosions and fires associated with electrical equipment.
Defining Intrinsic Safety Principles
Intrinsic safety revolves around the idea of controlling electrical energy to prevent ignition sources in hazardous areas. This involves using intrinsically safe devices designed to operate within strict parameters that limit voltage and current levels. The key principle here is that even under fault conditions, the energy released will not be sufficient to ignite an explosive atmosphere.
The ATEX standard plays a vital role in establishing these intrinsic safety requirements by defining acceptable levels of risk and outlining necessary design practices. For instance, cables wiring used in these applications must be specifically rated and tested to ensure they comply with intrinsic safety standards. By understanding these principles, designers can create systems that protect both personnel and property from potential hazards.
Applications in Hazardous Locations
Intrinsically safe designs find extensive application across various industries where hazardous materials are present—think oil refineries, chemical plants, and mining operations. In such environments, equipment like sensors and communication devices must be designed to minimize any risk of ignition while maintaining functionality. By implementing intrinsically safe equipment, companies can operate efficiently without compromising on safety.
Moreover, the use of proper electrical panel wiring is crucial when integrating intrinsically safe devices into existing systems. Each component must work harmoniously within the confines set by intrinsic safety standards while also being compliant with Class 1 Division 1 requirements for hazardous locations. This synergy ensures seamless operation in environments where every spark counts—literally!
Compliance with Class 1 Division 1 Standards
Compliance with Class 1 Division 1 standards is non-negotiable when dealing with intrinsically safe equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres. These standards specify areas where flammable gases or vapors may exist continuously or intermittently during normal operations—making it imperative for all equipment used here to meet stringent criteria for safety and performance.
To achieve compliance with these regulations often requires rigorous testing and certification processes—including ATEX certification—which validates that products meet internationally recognized safety standards for use in hazardous areas. Moreover, selecting approved cables wiring suitable for Class 1 Division 1 applications ensures that all components contribute positively toward overall system integrity and reliability.
In summary, understanding intrinsically safe requirements is foundational for anyone working within hazardous locations; it encompasses everything from fundamental principles of intrinsic safety to specific compliance mandates like Class 1 Division 1 standards—all aimed at safeguarding both people and property against catastrophic events.
Key Components of Intrinsically Safe Design
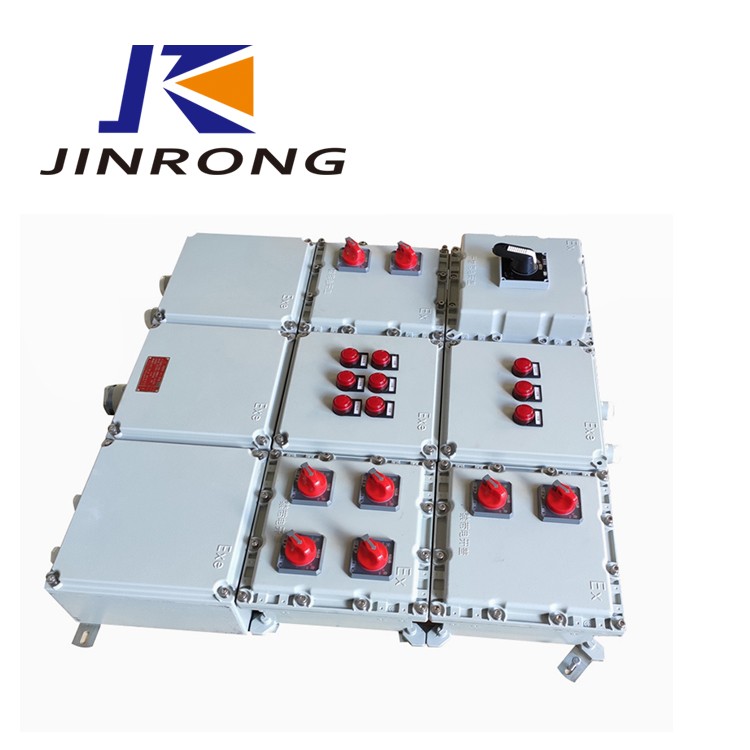

Essential Cables and Wiring Guidelines
Cables wiring is a fundamental aspect of any intrinsically safe system. The selection of appropriate cables is crucial; they must be designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions found in Class 1 Division 1 locations. Additionally, these cables should feature enhanced insulation properties and be capable of handling potential electrical faults without creating ignition sources, thus meeting the stringent intrinsically safe requirements.
Proper installation techniques are equally important when it comes to cables wiring. This includes ensuring that all connections are secure and that there is no risk of abrasion or damage from external factors. Following these guidelines not only ensures compliance with ATEX certification but also promotes a safer working environment for personnel who may be exposed to hazardous conditions.
Importance of Electrical Panel Wiring
Electrical panel wiring serves as the backbone of any intrinsically safe system, making its integrity paramount for safety. The design and layout of electrical panels must comply with intrinsic safety principles to prevent any risk associated with short circuits or equipment failures in hazardous locations. Properly executed electrical panel wiring minimizes potential hazards while ensuring functionality within Class 1 Division 1 areas.
Moreover, regular inspections and maintenance routines for electrical panels help identify wear or damage before they become critical issues. This proactive approach aligns with best practices for maintaining compliance with ATEX standards while keeping personnel safe from potential risks associated with faulty equipment or installations. Thus, investing time in proper electrical panel wiring pays dividends in both safety and operational efficiency.
Selecting Approved Equipment for Safety
Selecting approved equipment is a vital step in meeting intrinsically safe requirements within hazardous environments. Not all devices are created equal; hence it's essential to choose equipment specifically designed for intrinsic safety applications that comply with the ATEX standard. Using non-compliant equipment can lead to dangerous situations where ignition sources may arise unexpectedly.
Additionally, ensuring that all selected equipment has been tested and certified under relevant standards provides peace of mind regarding its performance in explosive atmospheres. Organizations should prioritize sourcing devices from reputable manufacturers who understand the intricacies involved in intrinsic safety design and adhere strictly to regulatory guidelines like ATEX certification. By doing so, businesses can create a robust framework for operational safety while minimizing risks associated with improper equipment use.
The ATEX Standard: An Overview
The ATEX standard is a crucial framework designed to ensure safety in environments where explosive atmospheres may occur. Originating from the European Union, it encompasses regulations that set forth intrinsically safe requirements for equipment and protective systems used in hazardous locations. Understanding the ATEX standard is vital for industries that operate under Class 1 Division 1 classifications, as it helps mitigate risks associated with electrical panel wiring and equipment.
History and Purpose of ATEX Regulations
The history of ATEX regulations dates back to the early 1990s when the European Union recognized the need for standardized safety measures in potentially explosive environments. The term ATEX originates from the French phrase Atmosphères Explosibles, reflecting its focus on preventing explosions through stringent safety protocols. The purpose of these regulations is to provide guidelines that ensure equipment meets intrinsically safe requirements, reducing the risk of ignition sources in hazardous areas.
Key Requirements for ATEX Certification
To achieve ATEX certification, equipment must adhere to specific requirements designed to ensure intrinsic safety in explosive atmospheres. This includes rigorous testing and evaluation of components such as cables wiring, ensuring they can withstand harsh conditions without compromising safety standards. Manufacturers are also required to provide clear documentation demonstrating compliance with Class 1 Division 1 standards, which governs how electrical devices should be constructed and maintained.
The Role of Jinrong in Meeting ATEX Standards
Jinrong plays a pivotal role in helping companies meet ATEX standards by providing high-quality equipment designed with intrinsic safety principles at their core. Their products undergo extensive testing to ensure they meet the necessary intrinsically safe requirements while maintaining performance efficiency in hazardous environments. By focusing on reliable electrical panel wiring and certified components, Jinrong assists businesses in achieving compliance with both ATEX certification and overall safety goals.
Best Practices for Implementing Intrinsic Safety
Implementing intrinsic safety in hazardous environments is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a commitment to protecting lives and property. By adhering to intrinsically safe requirements, organizations can mitigate risks associated with electrical equipment in explosive atmospheres. Here are some best practices that can significantly enhance safety measures.
Conducting Risk Assessments
Risk assessments are the cornerstone of any effective safety strategy, especially when dealing with Class 1 Division 1 locations where the potential for explosions is high. These assessments should identify hazards related to electrical panel wiring, cables wiring, and other equipment that may not meet ATEX standards. Regularly updated risk assessments ensure that all potential dangers are addressed and that compliance with intrinsically safe requirements is maintained.
A thorough risk assessment involves evaluating existing systems and practices, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing necessary changes to enhance safety. This proactive approach helps organizations avoid costly accidents while ensuring that everyone involved understands the risks associated with their tasks. Remember, safety isn’t just about compliance; it’s about fostering a culture of awareness and responsibility.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance Routines
Conducting regular inspections is vital for maintaining compliance with ATEX certification and ensuring ongoing adherence to intrinsically safe requirements. Inspections should cover all aspects of electrical panel wiring, cables wiring, and other components used in hazardous environments to identify wear or damage before they become serious issues. A well-planned maintenance routine not only enhances safety but also prolongs the lifespan of critical equipment.
Scheduling routine checks allows teams to detect non-compliant equipment or faulty installations early on, reducing the risk of incidents significantly. Maintenance routines should follow manufacturer guidelines while also considering specific operational conditions unique to each facility. Staying ahead of potential issues through diligent inspection can save time, money, and possibly lives.
Training and Education for Personnel
Even the best systems can fail if personnel aren’t equipped with the right knowledge about intrinsic safety principles. Comprehensive training programs should be established to educate employees on intrinsically safe requirements as well as how to properly handle electrical panel wiring and cables wiring in hazardous locations like those covered by ATEX standards. This education empowers staff members to recognize risks and understand their roles in maintaining a safe working environment.
Training should include practical demonstrations alongside theoretical knowledge so that employees gain hands-on experience dealing with real-world scenarios related to intrinsic safety challenges they may face on the job site. Additionally, ongoing education ensures that personnel stay current on changes in regulations or advancements in technology related to ATEX certification standards over time. Investing in your workforce's understanding of these critical concepts ultimately enhances workplace safety culture.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Intrinsically Safe Operations

In the realm of intrinsically safe operations, avoiding common pitfalls can make all the difference between safety and disaster. Organizations often overlook crucial aspects that can lead to non-compliance with intrinsically safe requirements, jeopardizing both personnel safety and equipment integrity. By understanding these mistakes, companies can better navigate the complexities of electrical safety standards, including the ATEX standard.
Neglecting Regular Safety Audits
One of the most significant blunders in maintaining intrinsic safety is neglecting regular safety audits. Safety audits are essential for ensuring compliance with Class 1 Division 1 standards and identifying potential hazards before they escalate into serious issues. Failing to conduct these audits can lead to oversights in cables wiring or electrical panel wiring that might compromise the entire system's integrity.
Regular audits should not be seen as a mere formality; they are a proactive measure for reinforcing intrinsic safety principles within hazardous locations. By systematically reviewing equipment and operational practices against intrinsically safe requirements, organizations can spot non-compliant equipment or outdated practices that could pose risks. Remember, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure when it comes to electrical safety!
Using Non-Compliant Equipment
Another common mistake is using non-compliant equipment that does not meet ATEX certification requirements or other relevant standards. This oversight can stem from cost-cutting measures or simply a lack of knowledge about what constitutes approved equipment for hazardous environments. Utilizing non-compliant devices undermines all efforts made toward achieving intrinsic safety and exposes workers to unnecessary risks.
When selecting equipment for intrinsically safe operations, it’s crucial to ensure that all devices have undergone rigorous testing and certification processes in line with the ATEX standard. Non-compliance not only affects operational efficiency but also opens up organizations to legal liabilities and potential fines from regulatory bodies. Always prioritize quality over cost; investing in compliant equipment will pay off through enhanced safety and peace of mind.
Misunderstanding Safety Ratings and Classifications
Misunderstanding safety ratings and classifications is yet another pitfall that organizations must avoid when dealing with intrinsic safety protocols. Many professionals confuse different classifications or fail to grasp their implications on operational procedures and equipment selection, leading to dangerous misapplications in hazardous areas. This misinformation can result in improper installation of cables wiring or electrical panel wiring that do not adhere to required specifications.
Understanding specific ratings associated with ATEX certification helps ensure that your operations align effectively with recognized standards for intrinsic safety. Each classification serves as a guideline for selecting appropriate tools and implementing necessary precautions within hazardous locations like Class 1 Division 1 areas. A solid grasp of these ratings will empower teams to make informed decisions about their operational setups while maintaining compliance with intrinsically safe requirements.
Conclusion

In summary, understanding intrinsically safe requirements is crucial for ensuring safety in hazardous environments. These requirements dictate the design and implementation of systems that prevent ignition sources, particularly in Class 1 Division 1 locations where flammable gases or vapors may be present. By adhering to these standards, industries can significantly reduce the risks associated with electrical installations.
Recap of Intrinsically Safe Requirements
Intrinsically safe requirements focus on limiting energy levels within electrical circuits to prevent sparks and overheating that could ignite flammable materials. This involves meticulous attention to cables wiring and electrical panel wiring, ensuring that all components are designed to meet stringent safety standards. Compliance with these requirements not only protects personnel but also safeguards equipment and facilities from potential disasters.
The Impact of ATEX Certification on Safety
The ATEX standard plays a pivotal role in enhancing safety by setting clear guidelines for equipment used in explosive atmospheres. Obtaining ATEX certification demonstrates a commitment to following intrinsically safe principles while utilizing approved equipment that meets rigorous testing criteria. This certification not only fosters confidence among operators but also promotes a culture of safety across industries engaged in hazardous activities.
Future Trends in Intrinsic Safety Technology
Looking ahead, advancements in intrinsic safety technology promise to further enhance compliance with intrinsically safe requirements and improve overall operational efficiency. Innovations such as smart sensors and IoT devices are expected to revolutionize how we approach electrical panel wiring and monitoring systems in hazardous locations. As industries continue to evolve, staying abreast of the latest developments will be essential for maintaining compliance with the ATEX standard and ensuring the highest levels of safety.

